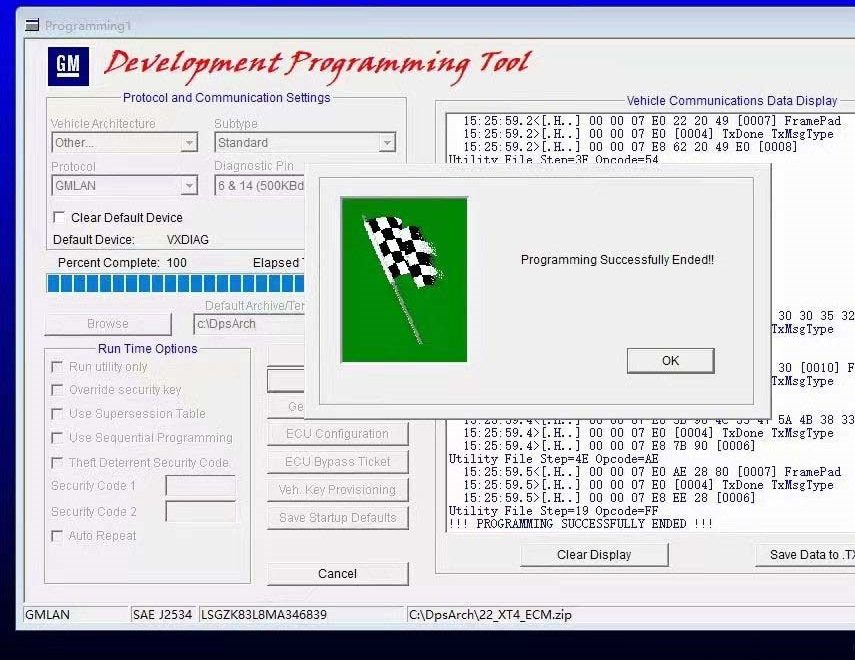
DPS (Development Programming System):
- Purpose: Internal software used by GM engineers to develop and program electronic modules.
- Functionality: Similar to the GM SPS (Service Programming System) client, but more versatile. DPS allows manual programming of standard or modified calibration files, changing VINs, PINs, and mileage on GM vehicle modules, as well as removing anti-theft features from radios.
- Requirements: Requires a compatible GM OBD diagnostic interface (e.g., VXDIAG VCX NANO GM, DrewTech Mongoose Pro GM2, or GM MDI-2) and access to GM SPS services for calibration files.
- Special Features: Offers advanced control such as unlocking anti-theft devices, changing module information (e.g., VIN/PIN), and manually programming modules without GM’s PLC services.
GDS2 (Global Diagnostic System 2):
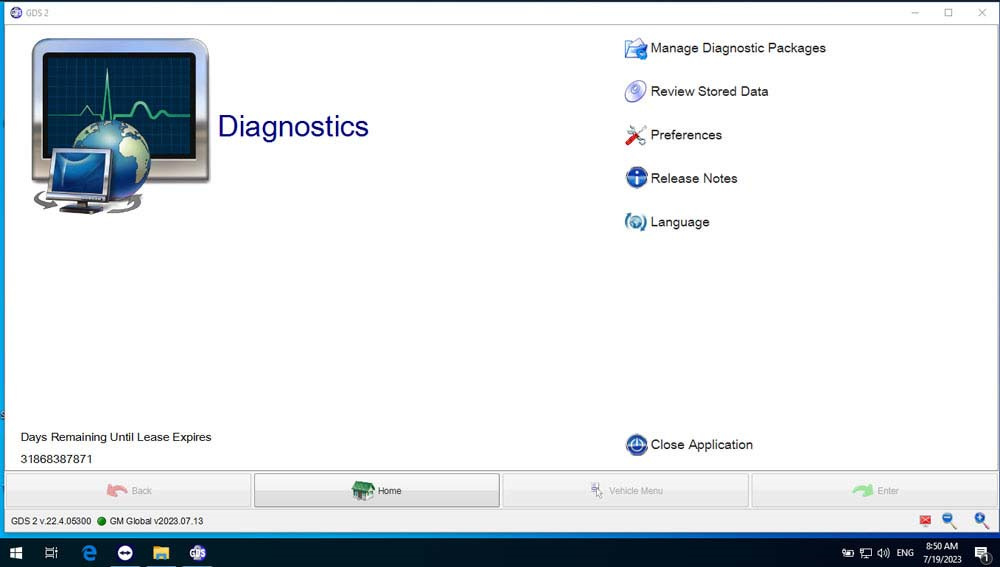
- Purpose: A PC-based diagnostic tool used by technicians for diagnosing and repairing GM vehicles’ electronic systems.
- Functionality: Primarily focused on diagnostics, offering features such as displaying data in graphs or units, performing simple DTC checks, starting manual DPF regens, and programming injector flow rates when replacing injectors.
- Requirements: Works with GM MDI or J2534-2 compatible interfaces (e.g., VXDIAG VCX NANO GM, GM MDI2).
- Special Features: Focuses on diagnostics rather than programming, with user-friendly features for efficient troubleshooting.
In summary, DPS is a more advanced programming tool designed for module development and custom reprogramming, while GDS2 is primarily a diagnostic tool used for repairs and basic module setups.