This guide outlines the steps to perform a mechanical cylinder compression test on a Detroit DDC-SVC-MAN GHG17 heavy-duty engine. Note: This test should only be performed if directed by a diagnostic procedure.
Related Contents:
2024.09 Detroit Diesel Diagnostic Link DDDL 8.20 8.09 Free Download
JPRO DLA+ 2.0 Adapter
NEXIQ USB 3 Link Adapter
Preliminary Considerations
Before performing this test, investigate the following possible causes of engine issues:
- Jake Brake/piston damage
- Valve lash/valve train damage
- Camshaft timing issues
- Cylinder liner/ring damage
- Fuel injector hold-down failure
- Blown cylinder head gasket
- Cracked cylinder liner or head
- Valve or seat damage
Relative Cylinder Compression Test
Important: Conduct a Relative Cylinder Compression Test using DiagnosticLink first. If results indicate a weak cylinder, proceed with the mechanical compression test as described below.
Mechanical Compression Test Procedure
- Check Valve Lash
Ensure valve lash is within specifications before starting the test. Refer to the “Setting the Valve and Engine Brake Lash” section for instructions. Adjust as necessary. If no adjustment is needed, proceed to step 2. - Warm Up Engine
Run the engine until the coolant temperature reaches normal operating range (88–96°C / 190–205°F). - Disconnect Batteries
Disconnect the batteries and connect them to a charger, following OEM procedures. - Remove Rocker Cover
Refer to the “Removal of the Rocker Cover” section. - Remove Fuel Injector Harness
- Remove the fuel injector harness.
- Disconnect electrical contacts from the fuel injectors.
- Disconnect the two wiring terminals on the Jake Brake® solenoids.
- Disconnect the 14-pin fuel injector harness connector.
- Remove the spring clip securing the injector harness connectors to the camshaft housing.
- Remove the fuel injector wiring harness(es).
- Remove High-Pressure Fuel Lines
Follow the “Removal of the High-Pressure Fuel Injector Lines – Two-Filter System” section. - Remove Fuel Injectors
Refer to the “Removal of the Fuel Injector – Two-Filter System” section. - Remove Residual Fuel
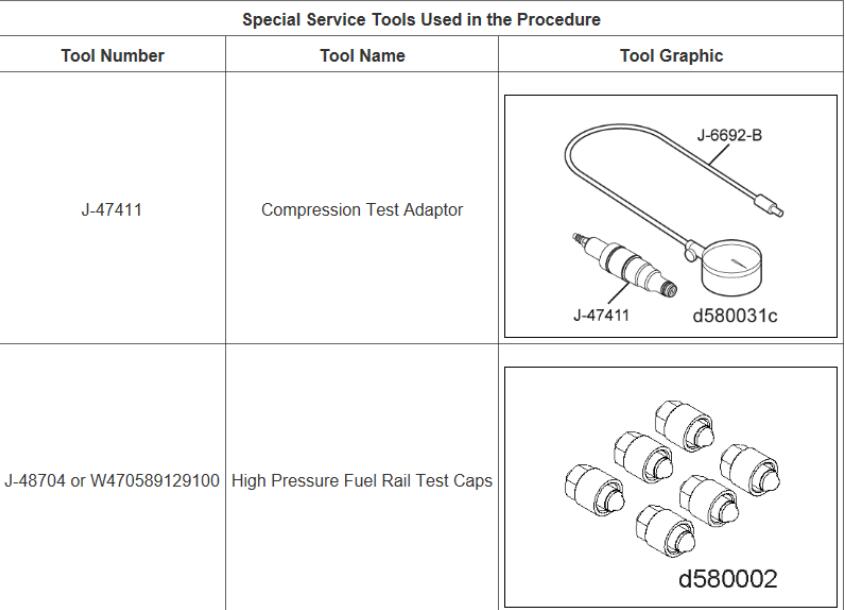
Use a vacuum pump to remove excess fuel from the cylinders. - Install Compression Test Adapter
- Install the compression test adapter (J-47411) into the injector bore in the cylinder head.
- Secure the injector hold-down clamp and bolt. Torque the bolt to 20 N·m (14 lb·ft) + 90 degrees.
- Plug the Fuel Rail
Install the fuel rail plug (J-48704 or W470589129100). - Secure Jake Brake Solenoid
Install a hold-down bolt on the Jake Brake® solenoid and tighten it. - Reconnect Batteries
Reconnect the batteries while keeping the battery charger connected.
Note: Ensure battery voltage remains sufficient to maintain engine cranking speed, as low voltage can affect test accuracy. - Start the Mechanical Compression Test
Using DiagnosticLink, initiate the Mechanical Compression Test routine to disable fuel flow from the Quantity Control Valve. - Crank the Engine
- With fully charged batteries, crank the engine over 5 compression strokes at a minimum of 150 RPM using the starter motor.
- Record the compression reading on the gauge.
- Evaluate Compression Readings
- At normal operating temperature, compression readings should be no less than 28 bar (400 psi).
- If readings are below specifications, repeat step 8 with a different gauge to confirm accuracy.
Note: Fuel injector hold-down bolts are single-use components and must be replaced after removal.
-
- Reassemble Components
- Remove the injector hold-down clamps and discard the hold-down bolts.
- Remove the compression test adapters.
- Reinstall fuel injectors and all removed components as per the relevant procedures.
- Reassemble Components
- Test Additional Cylinders
Repeat the test for all suspect cylinders, following the same procedure. - Repair as Necessary
Address any identified issues according to engine repair guidelines.
More repair cases for Detroit Diesel engines,please refer to:Detroit Diesel Engine Repair