Diagnosing and repairing agricultural vehicles (AGVs) has evolved significantly, with modern vehicles containing numerous electronic control units (ECUs) that monitor and manage various systems. Understanding fault codes, or diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), is crucial for efficient repairs. In this article, we will explore the importance of fault codes and share some common AGV fault codes for popular brands like JCB, John Deere, Fendt, and Massey Ferguson.
What are Fault Codes?
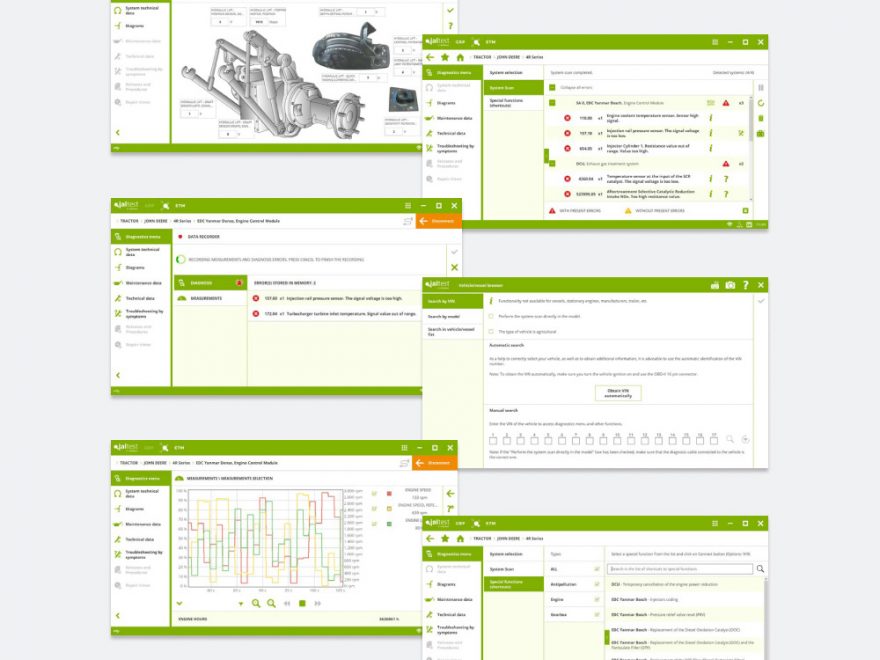
Fault codes are stored in a vehicle’s ECU and indicate specific malfunctions. Technicians can access these codes by connecting a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s onboard ports and running a system scan. Tools like Jaltest are advantageous as they use the same fault codes as the vehicle manufacturers, making diagnostics straightforward and universally understood.
How to Read AGV Fault Codes
The structure of a fault code can provide insight into the issue:
- First Number: Indicates whether the error is manufacturer-specific or applicable to all systems.
- Last Three Numbers: Provide details about the specific electrical circuit and system.
Jaltest users benefit from fault code descriptions that offer clear explanations of the fault and the related system, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Common Fault Codes
Here are some common fault codes for agricultural vehicles from JCB, John Deere, Fendt, and Massey Ferguson:
- CIS Error Code E-41
- Fault Description: Ground drive variable displacement motor solenoid coil (Y144) defective.
- Operation Condition: Restricted operation; driving at max 7 km/h in 1st gear, 12 km/h in 2nd gear.
- Remedy: Check and measure resistance of solenoid coil Y144, and replace the module if faulty.
- Error Code E-46
- Fault Description: Ground speed control lever potentiometer (R39) defective.
- Operation Condition: Emergency operation; machine moves at approx. 1 km/h only in a forward direction.
- Remedy: Check supply voltage and wiring of the potentiometer, and replace if defective.
- Fault Code E-196 EFA
- Fault Description: No signal from ground drive hydraulics reverse high-pressure sensor (B98).
- Operation Condition: Restricted operation; driving at max 7 km/h in 1st gear, 12 km/h in 2nd gear.
- Remedy: Check cable connections and pressure sensor, replace if needed.
- Fault Code E-199
- Fault Description: Ground speed control lever neutral – safety start switch actual value switch (Z57-2) not recognized.
- Operation Condition: Machine cannot be driven.
- Remedy: Check linkage, fixing, and settings, and verify the signal of the safety start switch.
- BRC 524016.04 – Front Brake Control Unit
- Fault Description: Secondary braking system fault.
- Possible Causes: Wiring issues, low supply voltage.
- Remedy: Check wiring, replace fuse F24, and test solenoid.
- SFA 524016.04 – Front Suspension System
- Fault Description: Low supply voltage to front axle direction solenoid, weak power steering, and non-adjustable suspension.
- Possible Causes: Disabled SFA, low battery voltage.
- Remedy: Check battery/alternator, clear fault codes, and perform alternator check.
- T 6145 X15 – PTO Clutch Speed Sensor
- Fault Description: X15 – PTO clutch speed sensor issue.
- Possible Causes: Speed selection issues, clutch slippage.
- Remedy: Check sensor and related components.
- A/C Fault 24
- Fault Description: Engine speed error due to invalid CAN message.
- Possible Causes: No valid CAN message within 2 seconds.
- Remedy: System defaults to 1500 rpm if no message is received.
- Fault Code 1.2.07
- Fault Description: Charge air temperature/boost pressure sensor signal error.
- Possible Causes: Sensor signal out of range.
- Remedy: Check and replace sensor if needed.
- Fault Code 1.2.94
- Fault Description: ECU EMR2 internal processing error.
- Remedy: Reload data record or replace ECU EMR2 if error persists.
- Fault Code 4.1.41
- Fault Description: Engine speed hall sensor 2 signal fault.
- Operation Condition: Emergency mode operation possible.
- Remedy: Check 12V supply and fuse A013.
- P3424
- Fault Description: SCR catalyst status is very high.
- Possible Causes: Unsuccessful SCR running refresh.
- Remedy: Perform exhaust after-treatment catalyst refresh procedure.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and diagnosing fault codes is crucial for maintaining and repairing modern agricultural vehicles. Tools like Jaltest provide comprehensive diagnostics and dealer-level access, making the repair process more efficient. By familiarizing yourself with common fault codes and using advanced diagnostic tools, you can ensure your agricultural vehicles operate smoothly and reliably.