What is a catalytic converter?
The catalytic converter is one of the most integral parts of your Mercedes, as it makes it safer to drive for you, those around you, and for the environment. The sole purpose of the catalytic converter is to reduce vehicle emissions and pollution.
Inserted in to the exhaust system, this metal canister is filled with a chemical catalysts, most commonly a mixture of platinum and palladium, which it uses to convert harmful emissions from the combustion process into safer, less harmful gasses, which are then emitted by the exhaust. Put simply, you have a little chemical lab in the exhaust of your Mercedes, and you probably never even knew about it.
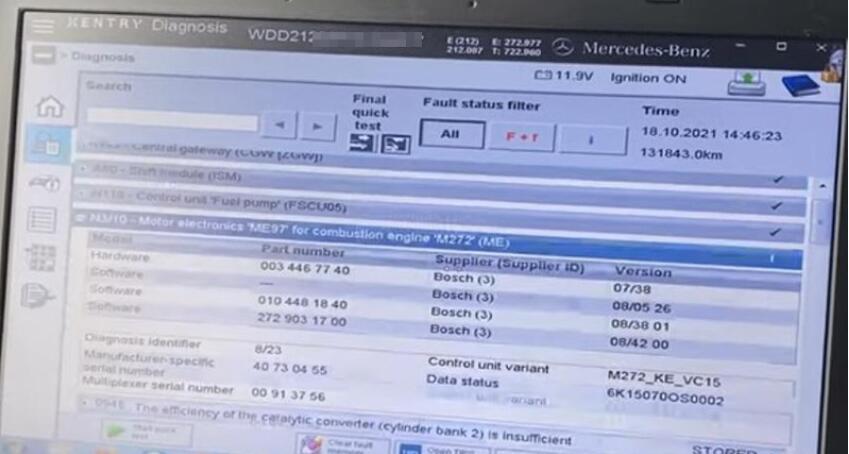
How to use Xentry to Check Mercedes-Benz Catalytic Converter Status

There are two catalysts worth doing a quick test and I’ll show you some interesting values. Many adapters are used to connect Mercedes to the PC to run the original Xentry software: Super MB Pro M6, VXDIAG VCX SE, SD C4 Plus
1.Check if catalyst is working
Go to engine control unit.
Don’t forget to check “I confirm that I have read the safety information”.
Start the car and switch to “Actual values”.
Unfold “Check combustion engine while idling”, we would find two values – Lambda control upstream/downstream of catalytic converter, that is the upper/lower sensor.
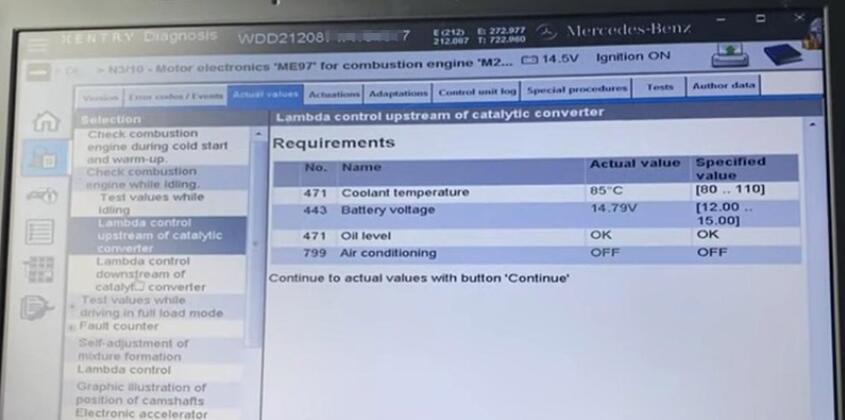
To see how the upper sensor work, select it and click on “Continue”.
Select these two options and display the bar graph.
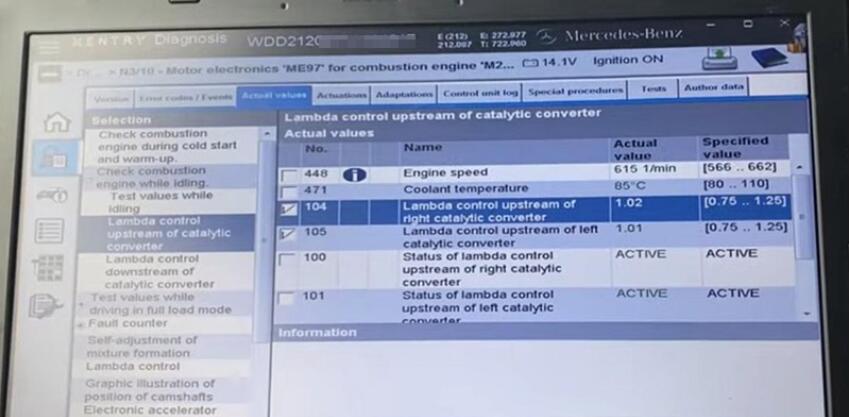
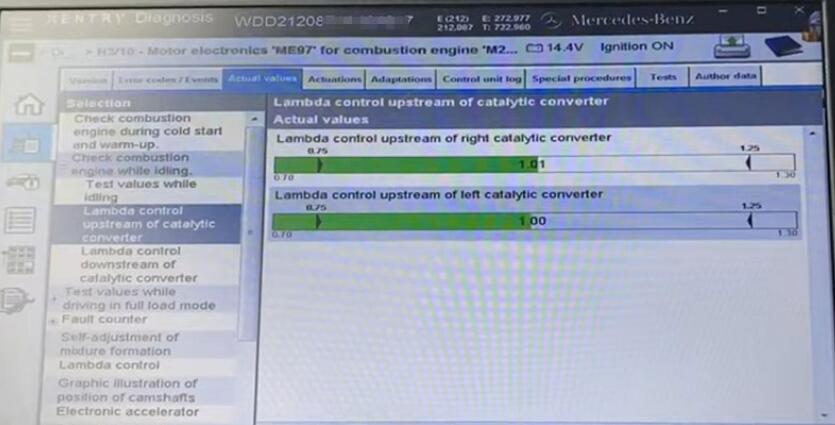
As the values fluctuate around the acceptable range, everything is normal, and the left and right block of cylinders is going on.
2.Check catalyst efficiency
Then select another option – downstream, which is for checking the efficiency of the catalyst, instead of if they are working like before.
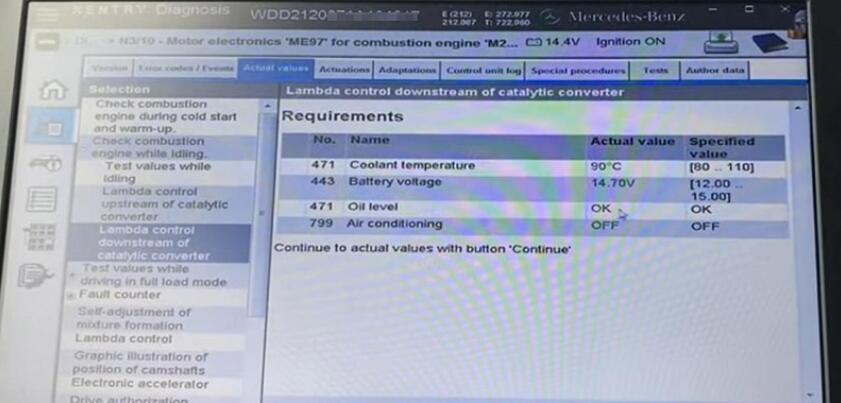
Enter its menu and check the left and right sensors to display its line graph.
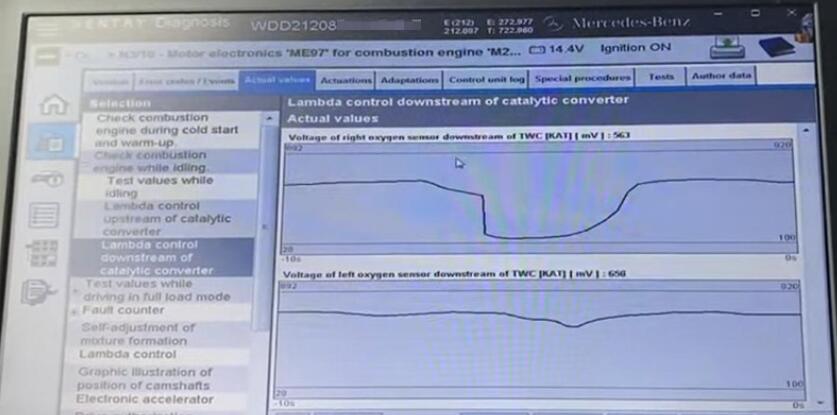
The catalyst here is much lower and higher. We cannot know what happens only by these graphs.
3.Check oxygen supply in catalyst
1)Gas temperature
So now we’re about to do a catalyst test.
Go to tests and scroll down to check oxygen supply in the catalyst.
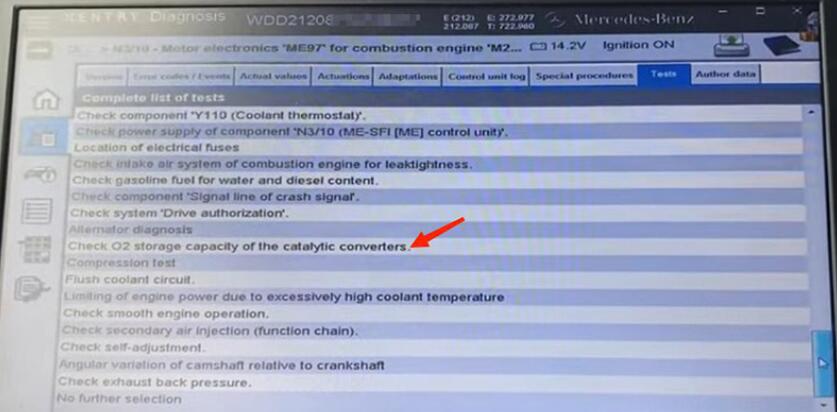
Idle the engine and switch off all consumers as required and continue.
Now we see the temperatures should be slightly adjusted by gas pedal.
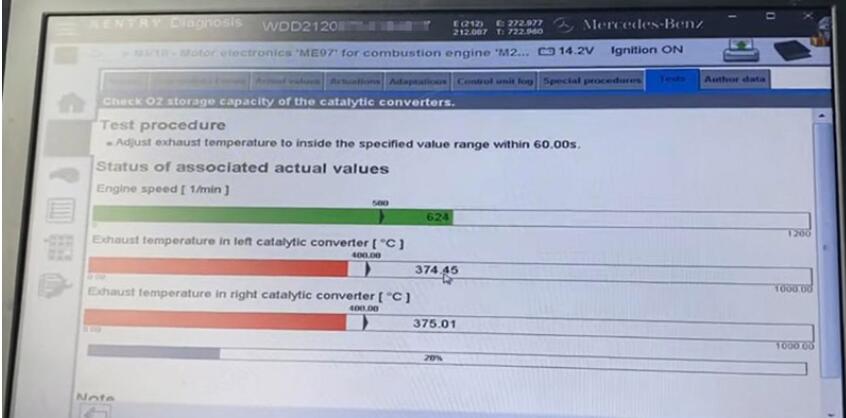
So we press the gas pedal until everything is green.
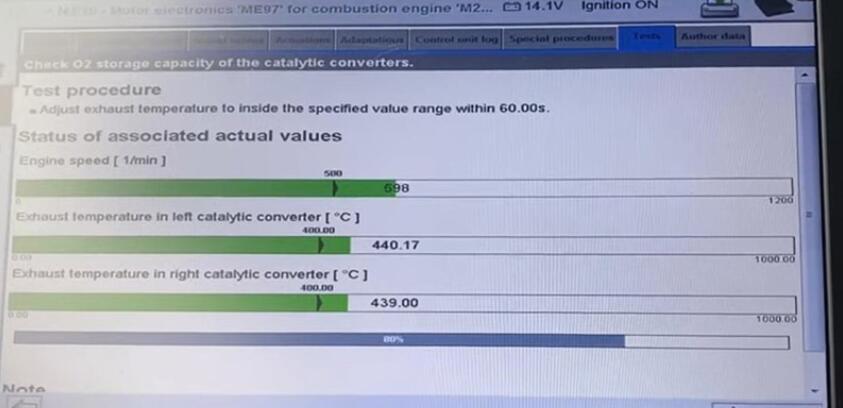
2)Gas volume
Continue to the next step – Exhaust volume that flows through the catalysts.
Start of evaluation ACTIVATED.
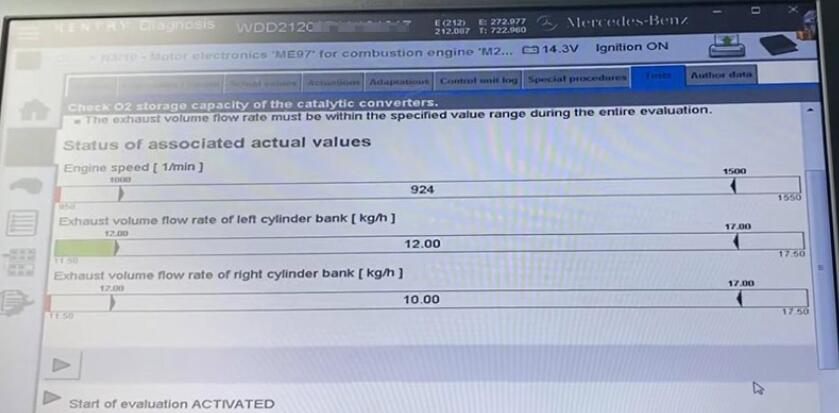
The result is not comprehensive, but it’s a measurement of oxygen in the catalyst converter.
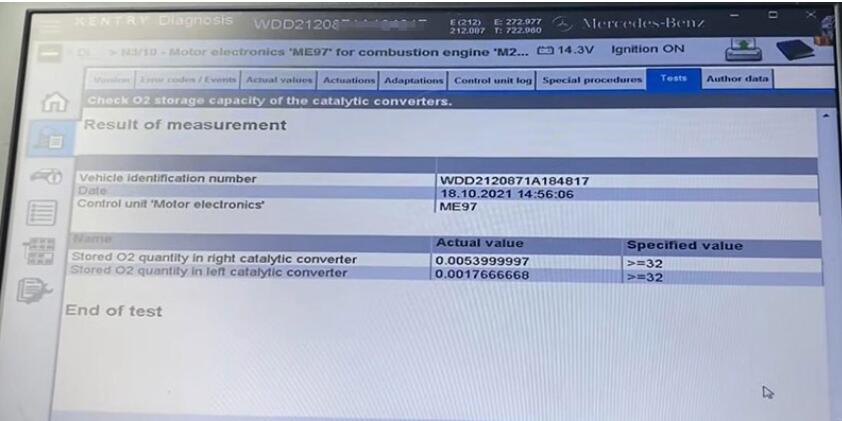
The oxygen supply in the left part is much lower than in the right, but from the previous graph we can see that the left part is overestimated.
Then back to Test menu and right/left oxygen sensor upstream tests are available.
As a consequence, with the left catalytic converter, something is wrong or missing, we need to check it with a scope.
After all, the numbers are inconclusive. Which unit and which coefficient are possible. You have to look at and compare many machines, like the brake pedal on the floor and the gas in the catalytic converters.